Max66, Arsgroup777, ARS Group Exchange: The aging process is a natural phenomenon that affects every living organism. As individuals grow older, various changes occur in their bodies, leading to a decline in physical and mental capacities. These changes often manifest in the form of wrinkles, reduced muscle mass, decreased cognitive function, and a weakened immune system. Despite the inevitability of aging, researchers continue to explore its underlying mechanisms to uncover potential interventions that could improve the quality of life for older adults.
One of the key factors contributing to the aging process is the accumulation of cellular damage over time. As cells divide and replicate throughout an individual’s lifespan, they are exposed to various stressors that can result in genetic mutations, protein misfolding, and oxidative damage. These cumulative insults eventually compromise the cell’s ability to function optimally, leading to the gradual decline seen in aging individuals. Understanding the intricate interplay between genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that influence cellular aging is crucial in developing strategies to promote healthy aging and prolong lifespan.
Factors Influencing Aging
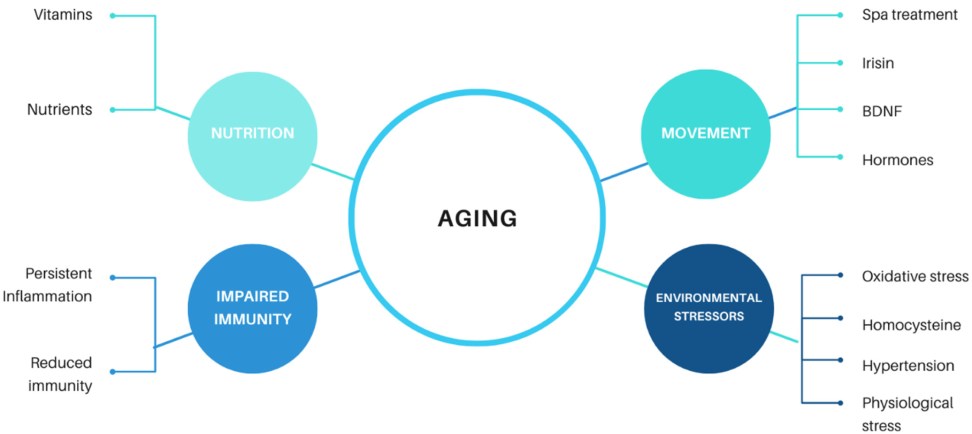
A variety of factors play a role in the aging process. One of the key influencers is genetics. Our genes can dictate how our bodies age and the potential health issues we may face as we grow older. Certain genetic variations may make individuals more susceptible to conditions like heart disease, cancer, or Alzheimer’s.
Another influential factor in aging is lifestyle choices. Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can all accelerate the aging process. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits can help slow down the effects of aging on the body.
Cellular Aging Mechanisms
Ars247, Wazeerexch, Peachexch: A key component of cellular aging is the gradual shortening of telomeres, protective caps found at the end of chromosomes. With each cell division, these telomeres get shorter, eventually leading to cellular malfunction and senescence. Additionally, the accumulation of oxidative stress within cells can cause damage to cellular structures and impair their normal functions.
Another significant mechanism of cellular aging involves the decline in mitochondrial function. Mitochondria play a crucial role in producing energy for the cell, and as they become less efficient over time, cellular energy production decreases. This decline in mitochondrial function can lead to an increase in reactive oxygen species production, further exacerbating cellular damage and contributing to the aging process.
� Telomeres, protective caps at the end of chromosomes, gradually shorten with each cell division
� Shortened telomeres can lead to cellular malfunction and senescence
� Accumulation of oxidative stress within cells can damage cellular structures and impair normal functions
� Decline in mitochondrial function is another significant mechanism of cellular aging
� Mitochondria are essential for producing energy for the cell
� Decreased efficiency in mitochondria leads to reduced cellular energy production
� Decline in mitochondrial function can increase reactive oxygen species production, causing further cellular damage
What is cellular aging?
Cellular aging refers to the gradual decline in the function and efficiency of cells as they age over time.
What are the main factors that influence the aging process?
Factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and oxidative stress can all play a role in influencing the aging process.
Can cellular aging mechanisms be reversed?
While some studies suggest that certain interventions like calorie restriction and exercise may slow down the aging process at the cellular level, reversing cellular aging completely is still a challenging task.
How does oxidative stress contribute to cellular aging?
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, leading to damage to cellular components like proteins, lipids, and DN
What are some lifestyle choices that can help slow down cellular aging?
Maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can all help slow down cellular aging.
Additional:
- How Many Jobs Are Available In Electric Utilities Central?
- How Many Jobs Are Available In Consumer Non-Durables
- How Many Jobs Are Available In Real Estate Investment Trusts?